L-GLUTAMINE is involved in many anabolic and mental processes in the body and in athletes it often strengthens the immune system weakened by the load during training. For the athlete, the most important thing is to know that the L-Glutamin molecule performs the so-called "nitrogen transfer function", i.e. the property of binding to other Amino Acids in the blood and transporting them to muscle cells. The regulatory functions of L-Glutamin are also well-known and especially popular with professionals. In other words, this is the ability to increase the volume of muscle cells at the level of insulin, HGH and cortisone. In everyday life, "stocking" our body with the amino acid is not at all difficult (it can be synthesized endogenously, i.e. by the body itself, through protein-rich nutrition).
However, a problem arises during and immediately after training. Due to the high peak loads, glutamine is invariably oxidized to obtain energy, and in significant quantities. Unfortunately, when taken orally, it enters the blood in very small quantities. One method of saving is to take 5 g of powder under the tongue (sublingual) and keep it there as long as possible. This increases the percentage of serum glutamine by 50%. As an alternative, athletes often use the sparing amino acid and well-penetrating BCAAs.
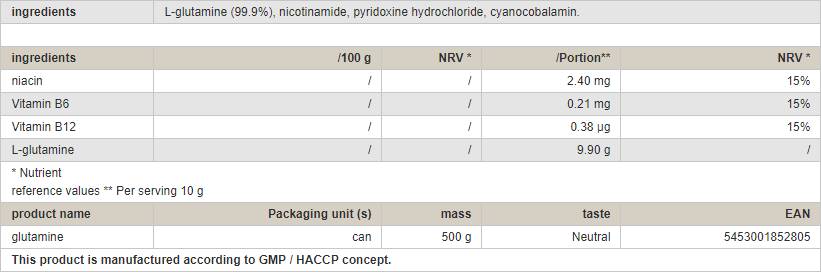
Directions for use: L-Glutamine - 10 g (about 1 tablespoon) dissolved in liquid, best immediately after training.